
A1C is a simple blood test that shows your average blood sugar (the results show an approximation of how much glucose bas been in your bloodstream) over the past two to three months.
Why Should You Know Your A1C levels?
It’s one of the most common ways healthcare professionals screen for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes (or a risk of developing type 2 diabetes). However, it’s also useful if you just want to understand how daily habits affect long-term health.
While only a lab test can accurately measure your A1C value (otherwise known as HbA1C), it’s also possible to calculate a general estimate of your A1C at home. In this expert-reviewed guide, you’ll learn:
- What the A1C test measures (in plain language)
- The difference between A1C levels and other glucose tests
- How to calculate your A1C from your average blood sugar or glucose
- What your results may mean for your health
- Nutrisense expert approved ways to track and improve your numbers
Plus, you can use our A1C Calculator below to estimate your level instantly.
What Does A1C Actually Measure?
The A1C test measures the amount of glucose bound to hemoglobin in the blood (or glycated hemoglobin) over the three month lifetime of your blood cells. Because red blood cells live about three months, your A1C reflects your average blood sugar over that time, not just one moment.
An A1C test result will appear as a percentage, with normal levels considered to be below 5.7 percent. According to the CDC, having A1C values within this normal range may be able to help reduce your risk of diabetes, with ranges typically interpreted as:
- Normal: below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7%–6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
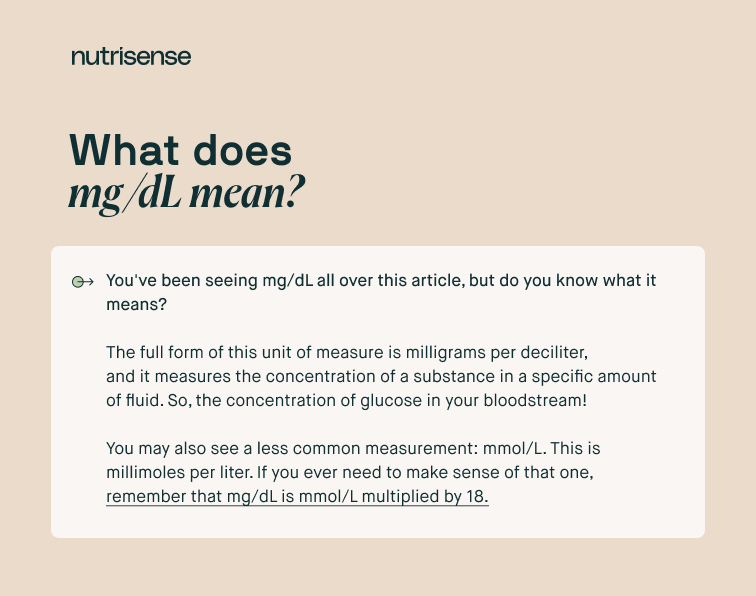
An A1C value differs from the glucose insights you would get from a glucometer, glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Measurements from these health-tech wearables and medical tools are reported in mg/dL or mmol/L, and can help you see:
- Instances of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) as they occur.
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) after eating a meal.
- Glycemic variability, or how your glucose fluctuates at present. A1C does not measure glycemic variability.
How Do You See an A1C Test on Lab Results?
Unlike cholesterol or routine blood tests, an HbA1C test usually needs to be specifically requested by your doctor (especially since it’s used as a way to diagnose prediabetes). It doesn’t require fasting, and results come back on your labs as a simple percentage.
Why track it? It can be helpful if your goal is to lower your elevated A1C levels to a more “ideal” range, but also if you want to maintain better long-term glucose control, or just get a check on your overall metabolic health.
The Difference Between Estimated Average Glucose and A1C
Your lab report may also show an estimated average glucose (eAG) alongside A1C. Here’s the difference:
- A1C (%) = % of a measurement of glycated hemoglobin in your blood, reported as a percentage of your average blood sugar level.
- Estimated average glucose or eAG (mg/dL or mmol/L) = an estimated average blood sugar value, calculated from your A1C value.
For example: An A1C of 5.7 percent corresponds to an eAG of about 117 mg/dL. For more information on what these values signify, read our comprehensive article on normal blood sugar levels.
7 Surprising Reasons Your A1C is High Even if You’re Not Diabetic
Feel like your A1C levels are high despite efforts to stabilize your glucose? These 7 surprising causes help you figure out why (plus, get expert tips to manage them)!
What is Estimated Average Glucose?
Like A1C, your estimated average glucose (or eAG) measures the average levels of your blood sugar over a few months. eAG is a measurement of mg/dL or mmol/L, the same units used on any glucometer or CGM. This is an estimate derived from A1C, and not a precise measurement. Here’s some interesting facts:
- Estimated average glucose that falls below 126 mg/dL is considered normal by researchers and medical professionals.
- Just like with A1C, regularly checking eAG may give you a more accurate representation of your response over time.
- eAG may not always correspond accurately to fasting glucose (FPG) levels. In a 2022 study published in Healthcare, researchers found that the proportion of subjects with a higher value of FPG than eAG was 46.3 percent in poorly controlled diabetic patients, compared with only 1.5 percent in normoglycemic subjects.
Why Should You Check A1C if You Already Know Your eAG?
Because A1C represents levels over an extended amount of time, you and your doctor can use this to get a general idea of your blood sugar control. However, hemoglobin A1C is not a measure of the exact concentration of glucose in your blood. It is a measure of the percent of hemoglobin that has glucose bound to it.
Remember, there are some outside factors that may skew the accuracy of your A1C reading, such as certain medications, anemia, blood pressure, or chronic health conditions. If your A1C or eAG is out of the normal range, speak with a healthcare provider about what may be causing it.
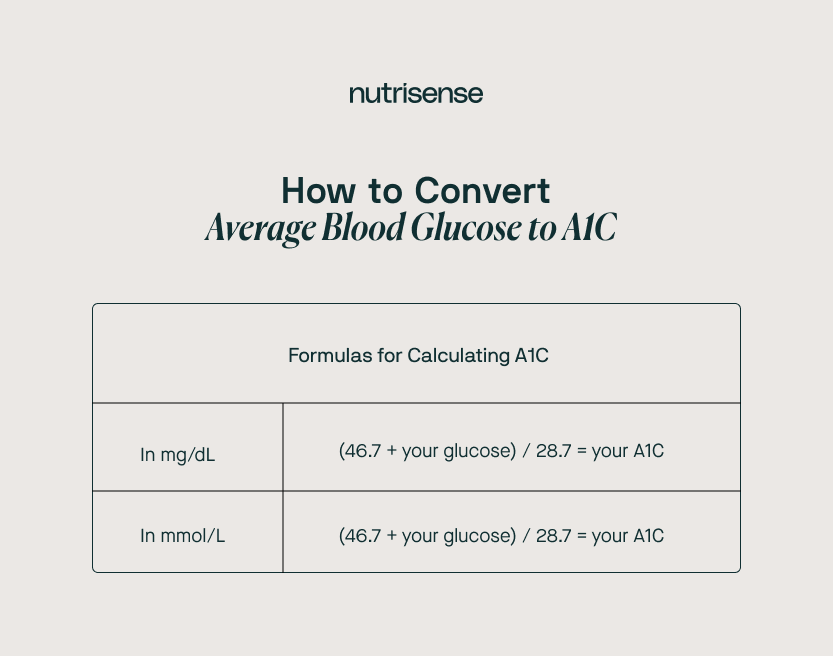
Converting Average Glucose Levels to A1C Levels
Now that you know what A1C is and what it measures, here’s how you can calculate it to estimate your A1C percentage using your average glucose level.
Did you know: Glucose is actually measured in different ways depending on where you live? In the United States, you’ll find levels measured in mg/dL, while other countries generally use mmol/L. To calculate your A1C value, apply your average blood glucose level measurement to one of the following formulas:
Try Our Free A1C Calculator
Now that you know what A1C is and what it measures, here’s how you can calculate it to estimate your A1C percentage using your average glucose level.
Now that you have your A1C value, let’s take a closer look at how you can understand it. Later, we’ll explain a few other ways you can test your A1C, either in a lab or at home.
Understanding Your A1C Level
Once you have an estimate of your A1C, check whether your levels are outside of the normal range by comparing your result to the ranges used by both the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the CDC as shown below. Remember, it’s only possible to see a rough estimate when calculating your A1C, as any calculator will use your eAG value to determine your A1C.
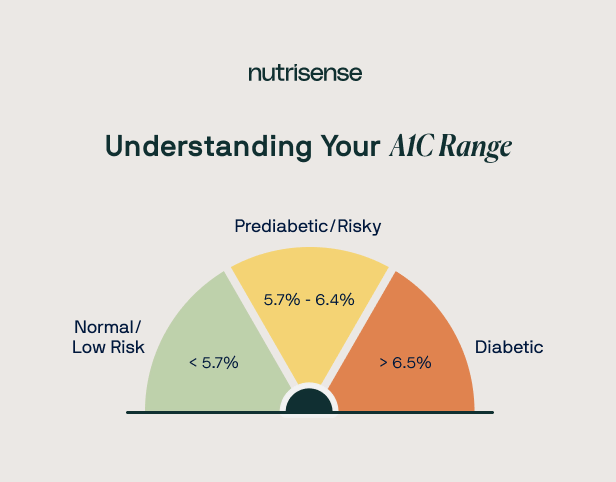
If your estimated range falls anywhere above 5.7 percent, you may want to consult a healthcare professional to make lifestyle changes to lower your levels over time.
And, as glucose expert Amanda Donahue, MS, RD, CD explains,
“Another way to detect imbalances and fluctuations in glucose to see its impact on your overall health is by using a tool such as a continuous glucose monitor, and working with a glucose-certified registered dietitian. If your A1C is out of the ideal range, you can use these patterns to work with professionals and glucose experts, to then set an A1C goal that works for your body.”
Now let’s take a closer look at how you can understand your A1C calculation, and a few other ways you can test your A1C, either in a lab or at home.
How to Calculate A1C Levels: 4 Easy Ways

Using Your Average Glucose Value From a CGM
Most wearables like biosensors or CGMs can provide you with a 30, 60, or 90-day average of your glucose readings over a chosen period. Using our handy calculator above, you can calculate an estimation of your A1C from the glucose data collected by your biosensor or CGM.
However, don’t depend on average glucose readings from a CGM alone. You also need to reference this with a fasting glucose lab value for more accurate baseline or average glucose depiction. Also, use a good companion app! Some apps, such as the Nutrisense App, even provide you with your average glucose based on your sensor readings.
Calculating Your A1C From Your eAG
If you already know your eAG level from a doctor's visit or another blood test, you can calculate your A1C from your average blood glucose reading using the calculator or formulas above.
{{rich-text-cta-member-stories="/style-guide"}}
A1C Home Tests
Options for telehealth and remote doctor visits have never been more popular. To meet the demand, many lab tests now have comparable analogs available to consumers. This includes at-home A1C tests, which can be as accurate as lab tests prescribed by your doctor. The bells and whistles can vary with the cost, so we recommend shopping around to pick what’s best for you and your needs.
A1C Lab Tests
Lab tests are some of the most common and reliable ways to get A1C results. There’s the traditional route, with lab work tests prescribed by a doctor, and there are also on-demand lab tests where outside doctors sign off on the tests without direct consultation.
Wherever you choose to get them, it may be a good idea to go over the results with a registered dietitian or doctor.
Quick FAQs and Key Takeaways
What is a normal A1C?
An A1C level below 5.7 percent is considered normal.
Can you calculate A1C at home?
Yes! Use our calculator with your average glucose or try an at-home A1C test kit.
Is A1C the same as a blood sugar test?
Not exactly. Blood sugar and glucose tests (like with a blood glucose monitor, or a continuous glucose monitor) often show your glucose at one moment, and help you track patterns over time. A1C tests show your average over two to three months.
How often should I test my A1C?
Most doctors recommend once or twice a year if you’re healthy, and more often if you have prediabetes, as part of your treatment plan for type 2 diabetes, or other risk factors.
Go Beyond A1C Tests with Nutrisense
“Since starting with Nutrisense, I noticed some incredible changes. My latest A1C went from 5.7 to 5.3.”
— Alejandro Ayestaran, Nutrisense Member
Knowing your A1C is a powerful first step. But it only gives you the average, not the why behind it. What you really need to tell the entire picture, is:
- Glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, to see how your body responds to food, stress, and sleep continually, not just every three months.
- Sessions (like insurance-covered video calls) with a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist to explain your numbers and guide next steps.
- An app or platform that can help you not just view your data but also follow the patterns, and help translate it into simple, actionable insights.
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you’ll get all this and more! So you can finally learn what’s stopping your health progress, and make informed lifestyle choices that support your goals. Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
Sign up for insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Find the right Nutrisense programto help you discover and reach your health potential.

Amanda is a Nutrition Manager and Registered Dietitian at Nutrisense, with a Masters in Dietetics from Stephen F. Austin State University. Originally from south GA, she got her undergrad degree from Texas Tech University. Before joining Nutrisense, she worked at a hospital in Fort Worth, TX, for 4 years as a dietitian, counseling those living with HIV.




