You’ve Been Diagnosed with Prediabetes – Now What?

Key Takeaways
Prediabetes is a condition where your glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be considered diabetes.
According to the CDC, approximately 96 million American adults (more than one in three) have prediabetes.
Of those with prediabetes, more than 80 percent don’t know they have it. If you've recently been diagnosed with prediabetes, you may be wondering what steps you can take to reduce the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes.
In this article, we’ll go into detail on what a prediabetes diagnosis means and what you can do to support your health. Read on to learn more.
What Is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a condition in which glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), prediabetes occurs when fasting glucose levels are between 100-125 mg/dL or A1C levels are between 5.7 and 6.4 percent.
Health Risks
Prediabetes can have significant effects on your life. If left untreated, it can progress to type 2 diabetes, which can cause complications such as nerve damage, kidney damage, and vision loss.
Symptoms are Often Subtle
People with prediabetes are at an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, such as a heart attack and stroke. Symptoms of prediabetes can be subtle and may not be noticeable at first, and many people may not experience any symptoms at all.
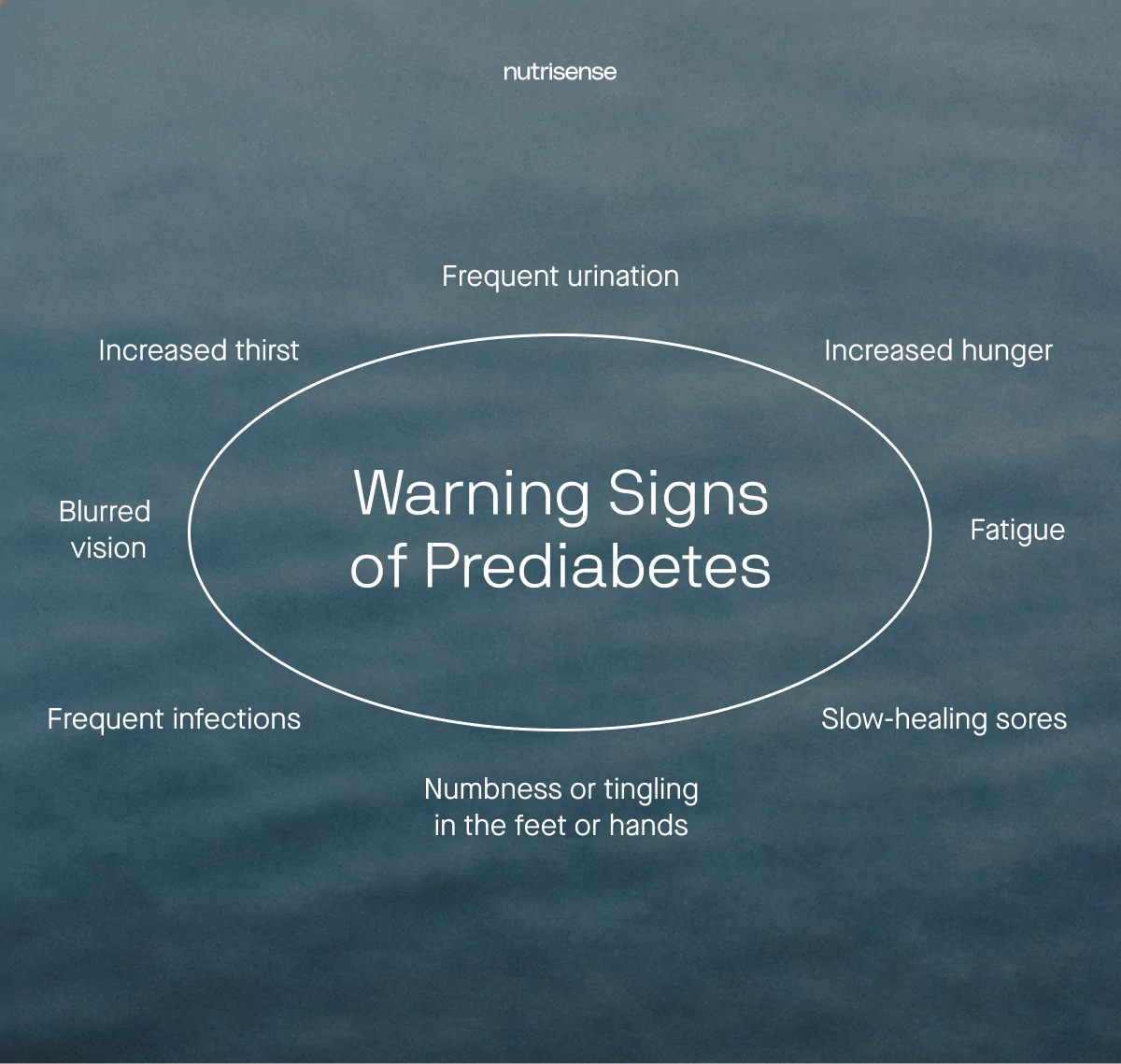
Warning Signs
This condition can only be diagnosed by a doctor through glucose level testing. However, there are certain warning signs that prediabetes has progressed to type 2 diabetes, and these include:
- Increased hunger or thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
- Frequent infections or slow-healing sores
- Unintended weight loss
Lifestyle Changes
Living with prediabetes may require making significant lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity. These changes can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Reversal Potential
Prediabetes can be reversed in some cases with lifestyle changes and drug interventions, but it is important to work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan.
Insulin Resistance
Prediabetes often reflects insulin resistance. In insulin resistance, cells in the muscle, liver, and fat respond less to insulin produced by the pancreas, so the body needs more insulin to keep glucose in range. Over time, fasting and post-meal readings can trend upward.
Prediabetes can occur in different contexts. If your glucose is trending high despite nutrition and movement changes, ask your clinician about other contributors that may be worth screening for.
- Visceral fat around the abdomen
- Obstructive sleep apnea or disrupted sleep
- Hormonal conditions such as hypothyroidism, Cushing syndrome, or PCOS
- Medications such as steroids
Addressing these alongside daily habits can help you and your care team personalize next steps.
Who is at Risk for Prediabetes?

While anyone can develop prediabetes, there are certain people who may be at higher risk. Risk factors for prediabetes include:
- Being 45 years or older
- Being obese or overweight
- Having a family history of type 2 diabetes
- Living a sedentary lifestyle or being physically active less than 3 times a week
- A history of gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby who weighs over nine pounds
- Being African American, Hispanic or Latino, American Indian, or Alaskan Native. Some Pacific Islander and Asian American people are also at higher risk.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop prediabetes. However, being aware of these risk factors and making healthy lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing prediabetes and other health problems.
If you have any concerns about your risk of developing prediabetes, talk to your healthcare provider.
What Happens if You’re Diagnosed with Prediabetes
A diagnosis of prediabetes means that your glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. This diagnosis is an important warning sign that you may be at risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems.
When 'Prediabetes' Becomes Your Reality
You hang up after the call from your doctor’s office, the word “prediabetes” echoing in your mind. You’ve been so careful with your diet and committed to your morning walks, but the scale hasn't budged much, and now this. Seeing an A1C of 6.1 percent on your lab report feels confusing and discouraging.
It feels like a verdict, but you know it’s a warning. The question is, what’s the first real step you can take today to start turning things around?
As one member shares: “Having my Nutrisense Nutritionist as a kind accountability partner has made a difference for me. I enjoy each session because I learn something new each and every session.”
Testing Methods
Prediabetes is diagnosed through blood tests, which may include A1C tests, fasting glucose tests, or oral glucose tests. These tests should only be conducted in healthcare settings by qualified healthcare professionals.
Risk of Progression
It is estimated that up to 70 percent of people with prediabetes will eventually develop type 2 diabetes if they do not take steps to manage the condition.
Lifestyle Actions
If you are diagnosed with prediabetes, your doctor will explain treatment options and lifestyle changes that may help you manage your condition.
Some studies show that it is possible to reverse prediabetes with lifestyle changes, such as improving your eating habits, increasing physical activity, losing weight, and quitting smoking.
Talk to Your Provider
If you are diagnosed with prediabetes, talk to your healthcare provider about how to manage your condition and reduce your risk of developing complications.
7 Tips for Dealing with a Prediabetes Diagnosis

Being diagnosed with a health condition can be an emotional time. The good news is that there are many things you can do to support your health and prevent prediabetes from progressing to a diagnosis of diabetes.
Here are some tips for dealing with a prediabetes diagnosis and taking control of your health:
1) Learn the Causes
Educating yourself about the causes of prediabetes is an important step in understanding the condition and reducing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Your healthcare provider can provide you with information about prediabetes and its causes.
There are also many reputable sources of information on prediabetes available online. Look for resources from organizations such as:
- American Diabetes Association
- The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
2) Focus on Weight Management

Starting a weight loss journey can be effective when it comes to prediabetes. Not everyone who is diagnosed with prediabetes or diabetes will be overweight, but it is a common risk factor for both conditions.
If you are currently overweight, even a small amount of weight loss, equal to five to seven percent of your body weight, can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve glucose control in people with prediabetes.
For more information on weight management and weight loss, read our article on weight loss for beginners.
3) Quit Smoking
If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes, stopping smoking is an important step in managing your condition and reducing your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Smokers have a 30 to 40 percent greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes.
When you stop smoking, you may actually improve your body’s use of insulin, which can have a positive effect on your glucose levels. Quitting smoking can also benefit your overall health, improve your quality of life, and reduce your risk of developing other chronic diseases such as cancer, lung disease, and cardiovascular disease.
4) Keep it Moving
Exercise can be a powerful tool when it comes to prediabetes. Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and glucose control, and can also help you lose weight or maintain a healthy weight, which is important for managing prediabetes.
Exercise is good for your heart and can reduce your risk of developing cardiovascular disease, which is a common complication of prediabetes. However, it is also important to note that more exercise does not necessarily equate to better metabolic health.
In fact, over-exercising may have similar detrimental effects on your health as a sedentary lifestyle. Everyone’s body is different with different capabilities. Talk to your doctor to better understand how much exercise is appropriate to manage your prediabetes.
5) Eat a Well-Balanced Diet
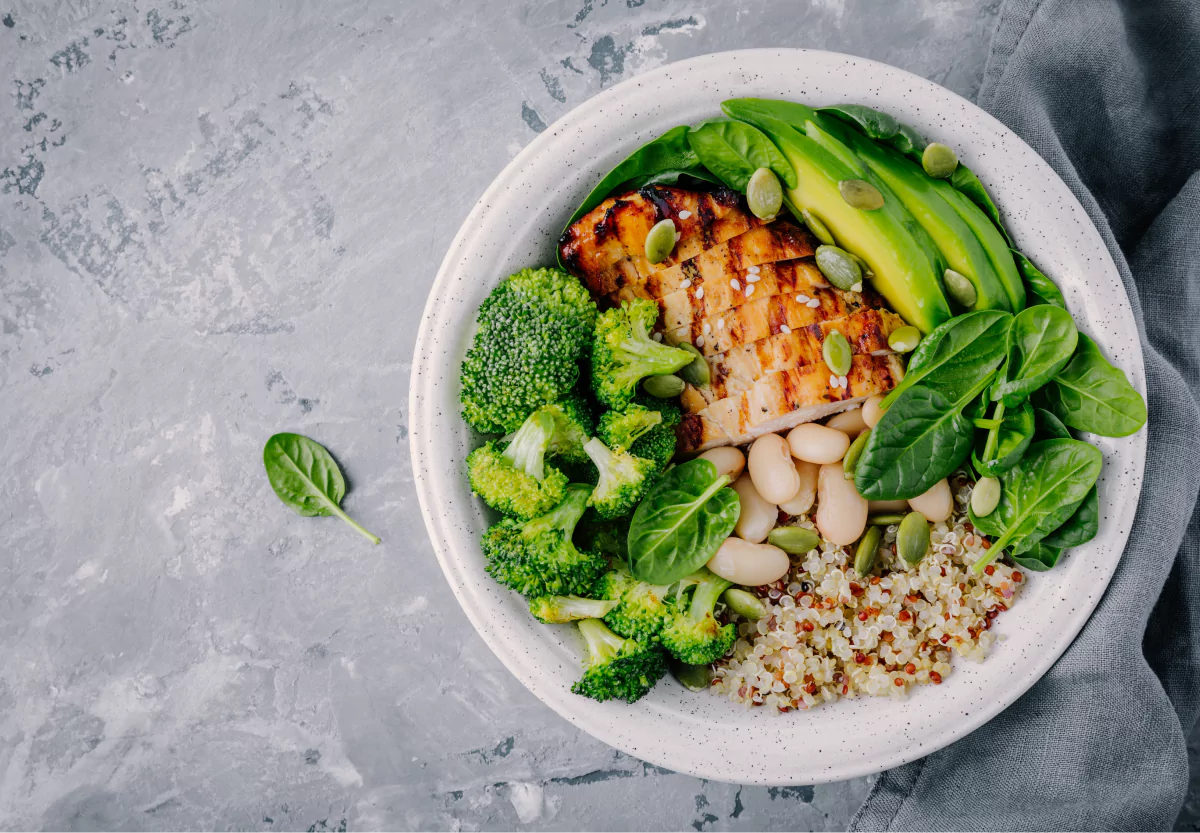

Following a diet high in refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can contribute to insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. Instead, try to practice healthy eating with a nutrient-rich diet.
This usually includes things like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats that can help support healthy glucose levels and prevent the progression of prediabetes to diabetes.
6) Reduce Stress
Stress can have a significant impact on prediabetes and glucose levels. Chronic stress has been shown to contribute to insulin resistance and the development of prediabetes and diabetes.
Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help improve glucose control and prevent the progression of these conditions.
7) Follow Your Recommended Plan
Following the recommended treatment regimen or lifestyle change program from your doctor is important for preventing the progression to type 2 diabetes. Your treatment may include dietary changes, exercise, and/or medication to help regulate glucose levels.
Top Exercises for Prediabetes

Exercise is an important part of managing prediabetes as it can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower glucose levels, and promote weight loss. Here are some top exercises for prediabetes:
- Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, is any activity that gets your heart rate up and increases your breathing. This can include activities such as brisk walking, hiking, jogging, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Strength training: Strength training, also known as resistance training, involves using weights or resistance bands to build muscle. This can help improve insulin sensitivity and promote weight loss. Aim for at least two sessions per week of moderate- or high-intensity strength training that targets all major muscle groups.
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest or low-intensity exercise. This can help improve insulin sensitivity and burn more calories in a shorter amount of time, and research shows HIIT can be beneficial for people with prediabetes or diabetes. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, so talk to your healthcare provider before starting.
Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise to avoid injury or overexertion. Always consult with your healthcare provider for guidance before starting any new exercise program.
The Glycemic Index and Prediabetes

How your diet affects your glucose is very important to keep in mind if you have prediabetes.
GI Basics
When you eat, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, and the glycemic index ranks how quickly this glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Foods with a high glycemic index are rapidly absorbed and cause a sharp rise in glucose levels, while foods with a low glycemic index are absorbed more slowly and cause a slower, more gradual rise in glucose levels.
Glycemic Load
A food’s glycemic load, which takes into account portion sizes and the amount of a food you are likely to eat, also plays a role in how food affects glucose. Research shows that following a low-glycemic load diet may help prevent the progression of prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
However, it's important to note that the glycemic index is just one factor to consider when making dietary choices. Portion size, total carbohydrate content, and the presence of other nutrients such as fiber, protein, and fat also affect how a food affects glucose levels. And remember that moderation is key: all foods can be part of a healthy diet in moderation.
Meal Ideas
If you’re in need of some glucose-friendly meal ideas that won’t spike your glucose, check out our article on a healthy diet plan for prediabetes.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
FAQs after a prediabetes diagnosis
Q1. Do I need a prescription or a diabetes diagnosis to start Nutrisense?
A1. No. You do not need a prescription or a diabetes diagnosis to join Nutrisense. The program supports wellness and metabolism training for people with or without diabetes. You will use a glucose biosensor and the Nutrisense app, with optional coaching, to learn from your 24/7 data and make habit changes that fit your life.
Source: CGM without Diabetes
Q2. How do Nutrisense sensors measure glucose?
A2. Nutrisense sensors measure glucose in interstitial fluid, the fluid between cells. This provides 24/7 trend data rather than single readings. You scan the sensor and view patterns in the app, then run food or activity experiments to see how your body responds so you can adjust your routine with support if you choose.
Source: How it works
Q3. Which app features are most useful right after a prediabetes diagnosis?
A3. After a prediabetes diagnosis, many members track time in range, average glucose, and glycemic variability in the Nutrisense app. You can log meals, exercise, and sleep to see what drives your unique responses, then review insights with a registered dietitian if desired. These features help you build practical daily habits.
Source: Nutrisense App
Q4. Are dietitian video calls covered by insurance, and how do I check?
A4. Yes, many members use insurance for video calls with registered dietitians. You can check eligibility online in minutes. Nutrisense accepts plans from major insurers across all 50 states, and sessions are often available with $0 out of pocket. You can also self-pay for sessions if preferred.
Source: Nutritionist video calls
Q5. How quickly can I get started after I sign up?
A5. Approval usually takes 1 to 2 days after signing up. Orders are processed in 1 to 2 days and shipped to US addresses, which typically takes 3 to 5 business days. While you wait, download the app and schedule your first nutritionist call so you are ready when your sensors arrive.
Source: How it works
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. With Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
Work with a Dietitian
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
The Nutrisense Program
With the Nutrisense Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.


.webp)

