Meal Frequency & Insulin Sensitivity: How Many Times Should You Eat in a Day?

Key Takeaways
The best meal rhythm for your body isn’t one-size-fits-all. Research shows both frequent meals and longer gaps can work; it depends on you. Both fewer, larger meals and more frequent, smaller meals can impact glycemic control, depending on the individual. The only reliable way to find what works? Seeing how your body actually responds. Because your “best plan” may not look like anyone else’s.
Highlights:
- Your metabolic rate and the thermic effect of food are influenced by meal frequency, which in turn affects your overall energy balance.
- Discover how your glucose levels respond to different meal patterns by tracking your body's data.
- The Nutrisense program, including biosensors and app access, is currently available within the US.
- Get 1:1 guidance from a registered dietitian to build a personalized plan.
The best meal rhythm for your body isn’t one-size-fits-all. Research shows both frequent meals and longer gaps can work; it depends on you. Both fewer, larger meals and more frequent, smaller meals can impact glycemic control, depending on the individual. The only reliable way to find what works? Seeing how your body actually responds. Because your “best plan” may not look like anyone else’s.
Highlights:
- Your metabolic rate and the thermic effect of food are influenced by meal frequency, which in turn affects your overall energy balance.
- Discover how your glucose levels respond to different meal patterns by tracking your body's data.
- The Nutrisense program, including biosensors and app access, is currently available within the US.
- Get 1:1 guidance from a registered dietitian to build a personalized plan.
Where do your eating habits fit?
We're all pretty different when it comes to dietary habits and eating patterns. Ever wonder if your eating pattern really fits your body, or if you’ve just been following advice that never quite sticks? For example:
- Are you the sort of person who eats three square meals a day, or do you prefer grazing?
- Do you incorporate physical activity into your post-meal routine, or do you choose a nap after lunch?
- Does your daily food intake involve a lot of snacking, or do you save that for special occasions?
From focusing on high-carbohydrate or low-carbohydrate meals to ensuring you get all your macronutrients, it’s no wonder meal planning feels confusing. Everyone says something different, and your body seems to have its own rules. If you’re not sure how often to eat, you’re not alone.

Why meal frequency matters
Many people struggle to find the right meal frequency and pattern to support their health goals. Meal frequency can affect everything from your body weight and glucose levels to other markers of metabolic health and overall well-being.
Of course, there are many opinions on how often you should eat. Some suggest that increased meal frequency can help with weight management or reduce disease risk. For example, there may be a reduced risk of obesity and cardiovascular disease.
What we do know is that maintaining consistent meal timing can be important for overall health and wellness. According to some research, the number of times we eat each day may significantly impact our insulin sensitivity and overall metabolic health.
So, with that in mind, here’s what you should know about the effect of meal frequency on your health.
What is insulin sensitivity?
Insulin sensitivity is essential for overall health, and it's something that you should be aware of if you're looking to manage your weight or glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps your cells take in sugar from the blood to use for energy.
Understanding insulin sensitivity and glucose responses to food and exercise is vital for everyone, but it is especially crucial for those with conditions that directly influence insulin sensitivity, such as hypothyroidism, type 1 diabetes, and type 2 diabetes.
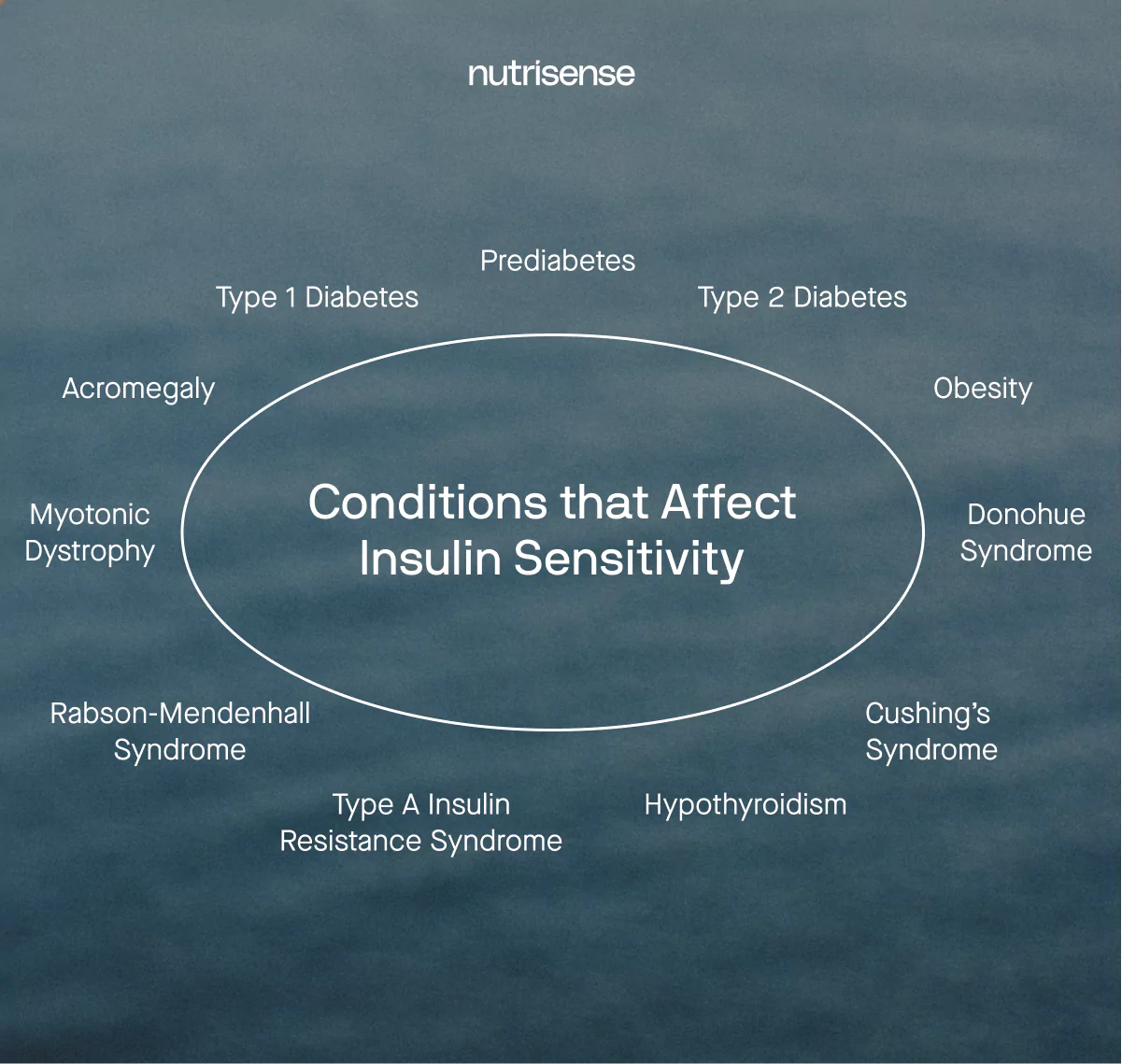
Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and lab markers to know
Insulin resistance means cells respond less to insulin. In the clinic, it is often discussed with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of cardiometabolic risk factors reviewed alongside common labs and vitals.
For clinical definitions and targets, see the ADA Standards of Care in Diabetes 2025, Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management.

Markers you may see in notes or labs:
- HOMA IR: An estimate of insulin resistance derived from fasting insulin and fasting glucose.
- HbA1c: Reflects average glucose over about 2 to 3 months.
- Hyperinsulinemia: Higher circulating insulin that can accompany insulin resistance.
- Hepatic fat content: Liver fat may be assessed with imaging or specialized tests as part of a metabolic evaluation.
- Metabolic syndrome factors: Central adiposity, triglycerides, HDL, blood pressure, and fasting glucose are often reviewed together.
If you use a biosensor, remember it reports glucose measured in interstitial fluid. For device fundamentals, see the ADA Diabetes Technology Standards 2025.
The 3 p.m. meal-timing puzzle
You ate a sensible salad for lunch, determined to stick to your plan. But now it’s 3 p.m., your energy is dipping, and you’re fighting the urge to snack. You question your strategy: Should you have a small snack to stabilize your glucose, or will that just cause another spike?
You've heard conflicting advice, from eating six small meals a day to just three larger ones. It feels like you're constantly guessing, trying to follow rules that don't seem to fit what your body is telling you.
How does eating impact insulin?
Eating has a significant impact on insulin levels, and the way you eat can either help or hinder your ability to maintain stable glucose levels. There are a few different schools of thought on meal frequency and its impact on glucose and insulin.
One popular option is to eat a few large meals throughout the day, while another is to eat four to six small meals each day. It’s challenging to pinpoint what the best move is here.
After all, research shows varying responses across studies among people with different conditions. It's a good idea to discuss your dietary goals, including meal frequency, with your doctor before making any changes.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
You might not need to eat less, just differently. See how your body responds to your meal rhythm.
You might not need to eat less, just differently. See how your body responds to your meal rhythm.
How eating two to three meals a day impacts insulin responses
Here are the pros and cons of eating larger meals less often, along with what you need to know about how meal timing affects your insulin response.
Pros of two to three meals

- When you eat later in the day, your body is less insulin sensitive. So, it’s no surprise that health professionals advise against eating large meals too late in the day. Eating two to three well-balanced meals earlier in the day can help you begin your overnight fast earlier in the evening and start again with an earlier eating window the following day.
- Some research shows that skipping a meal in the evening before beginning a fast may be an effective way to reduce weight and fasting glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
- According to some research, eating larger, more well-balanced meals less frequently may curb hunger. It may also provide more satisfaction than eating several small meals a day.
- When you eat less frequently, some believe you may give your pancreas a helpful break from producing insulin.
- Research has shown that beginning your day (or breaking your fast) with a large, high-energy meal helps optimize metabolic control.
Cons of two to three meals

- Research on short-term fasting has shown that it may initially cause spikes in glucose levels.
- In some cases, large meals can lead to large spikes in postprandial glucose levels. It may also often depend on what you’re eating during those meals.
- Some studies show that individuals who eat a single large daily meal have higher fasting glucose levels and impaired morning glucose tolerance, associated with a delayed insulin response, during a 2-month diet period, compared to those consuming the more frequent 3-meals/day regimen.
- Research shows that having a higher glycemic average over time, with relatively stable glucose levels, may be preferable to having dramatic glucose fluctuations with a lower average. Remember, this can vary from person to person. Using technology such as glucose biosensors or CGMs, and working with your doctor or dietitian, are excellent ways to investigate these connections more deeply.
How eating four to six meals a day impacts insulin responses
When you eat smaller meals throughout the day, your body releases insulin in response to those meals more often than if you ate only two to three larger meals. However, since these are smaller meals, the overall insulin release may also be much lower. Here are some pros and cons of this eating pattern.
Benefits of small, frequent meals

- Because your body may be more sensitive to carbs after breaking a fast, eating a smaller breakfast might be beneficial for some. So, starting with a small meal of protein and fiber before having carbohydrates may work better for your body.
- If you suffer from gastrointestinal issues like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), your doctor may advise eating small meals throughout the day. Certain health conditions, such as chronic fatigue, may be easier to manage with more frequent, smaller meals.
- Some studies even show that eating four meals per day, compared with three, was associated with a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This means that more frequent meals might have a positive impact on glucose and insulin response for some.
Cons of small, frequent meals

- It may be harder to create a fully balanced meal with small meals. If your meal isn't properly balanced, it could lead to glucose fluctuations after some meals.
- Though research is definitely conflicting in this area, some suggest that certain people might have lower glucose levels with fewer meals. Again, it may largely depend on what you eat during your meals.
How should you plan your meals?

Everyone’s metabolism plays by slightly different rules. The goal isn’t finding “the perfect schedule;” it’s finding yours. Still, there are guidelines that can be helpful.
At Nutrisense, we know there are many reasons your body may do better with more or fewer meals. Since research is conflicted and controversial about the exact number of meals that are best for everyone, it's important to be open to experimenting with different approaches to find what works best for your unique body. Tracking your glucose, symptoms, and meal patterns can help you find the answers you’re looking for.
However, a growing body of research indicates that eating fewer than 2 meals a day may be linked to greater stress activation in some people, including poorer glucose control and a higher risk of nutrient imbalances.
Is intermittent fasting right for you?
Some forms of time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting may be helpful for certain people. In some cases, your body may need more frequent meals throughout the day, depending on how your glucose levels react to larger meals.
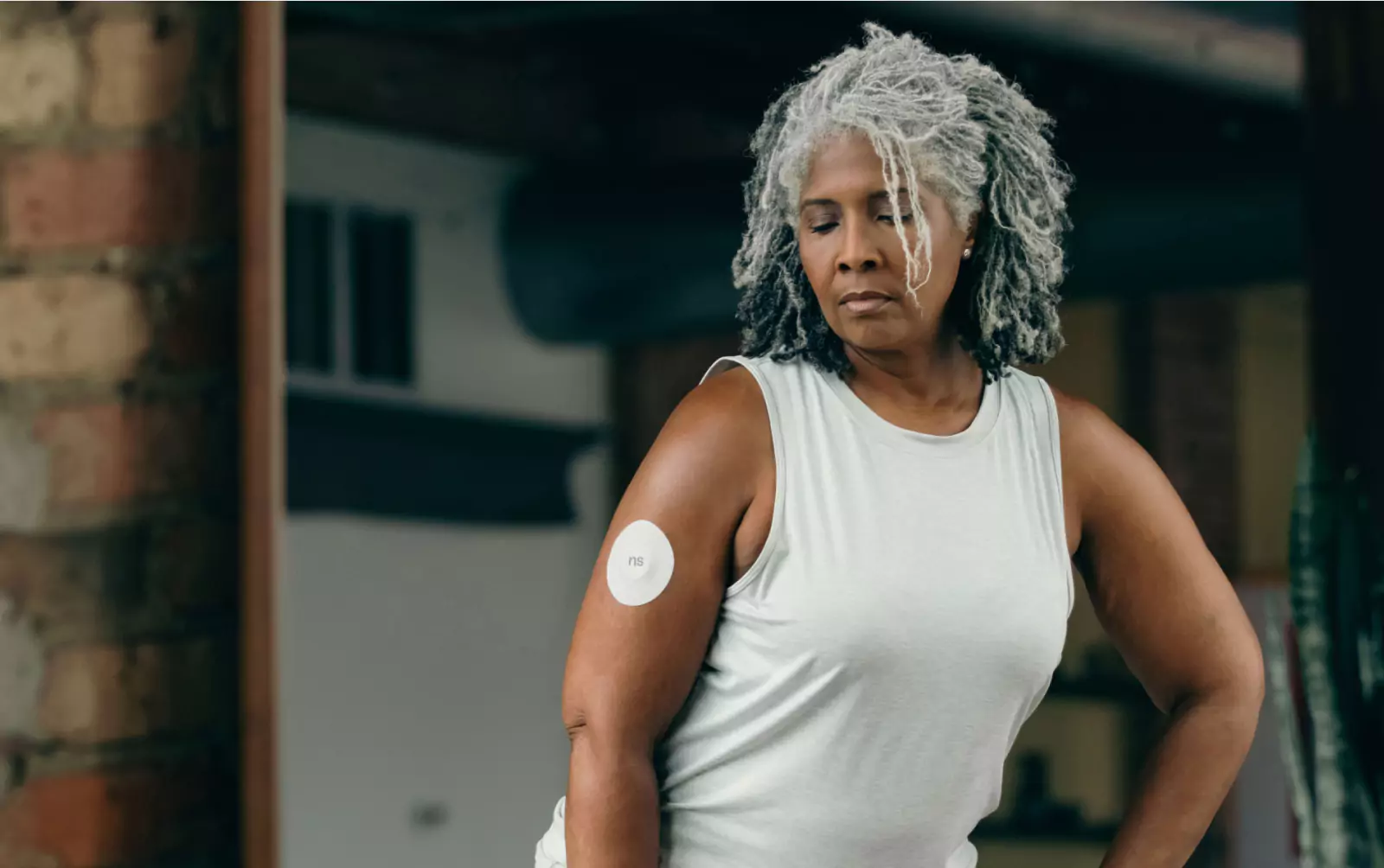

When to use CGM insights
Here's where wearable health technology like CGMs can be helpful. They measure your glucose trends over time so you can see which foods and meal sizes work best for your body.
Dietitian pro tips
- Eat intuitively and listen to your hunger cues. Your body will tell you when you are hungry and full. Try to balance your meals properly so your body gets the right messages from what you consume.
- Start your day with protein. Research shows that eating protein to break your fast in the morning can help you stay fuller throughout the day and boost your energy levels.
- Meal planning is a great way to ensure you're getting the proper nutrients and that your food expenditure is in check. Check out our meal-planning guide.
Meal frequency and insulin sensitivity FAQs
Q1. How can I use Nutrisense to compare two vs four meals per day?
A1. Wear your glucose biosensor and log every meal, portion, and activity in the Nutrisense App. Keep daily calories and macros similar across test days. Repeat each pattern for several days, then review peaks, post-meal curves, and glycemic variability. Add notes on hunger, energy, and sleep. If you want feedback, schedule a nutritionist call.
Source: What is a CGM App
Q2. Do I need a prescription, and how soon can I start?
A2. You do not need a prescription to sign up for a Nutrisense plan. If you sign up for the CGM plan, you get a monthly sensor shipment, access to the Nutrisense App, and the option to book dietitian video calls (insurance-covered based on eligibility) for additional guidance. You can also pick dietitian-coaching plans or bring your own sensor options to use with the Nutrisense App.
Source: How It Works
Q3. What do the sensors measure, and how often do they record data?
A3. While this depends on the sensor and model you use, most glucose biosensors and CGMs measure glucose in interstitial fluid. Readings are captured about every 15 minutes for a continuous 24/7 view of your trends. You can bathe or swim with the sensor to about 8 feet. Avoid extreme heat or cold. Pair it with the Nutrisense App to see patterns after meals, activity, and sleep.
Source: What is a CGM
Q4. Can a Nutrisense dietitian help adjust my meal timing and snacking?
A4. Yes! Nutrisense’s registered dietitians and certified nutritionists are glucose experts who have helped over 150,000 people optimize their diets. You can book insurance-covered (based on eligibility) video calls for ongoing guidance. Your dietitian reviews everything from your habits and likes and dislikes, to your stress levels and meal timing, to create a plan that suits your daily reality. The guidance is diet-agnostic and personalized to your data and goals.
Source: Nutritionist Video Calls
Find out how many times you should eat with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall well-being. But viewing glucose isn't enough. With Nutrisense, you’ll learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
Work with a dietitian
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
24/7 glucose insights
With the Nutrisense Program, you can monitor your glucose using health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and analyze trends over time in the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Ready to take the first step?
Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Kara Collier is a registered dietitian nutritionist and certified nutrition support clinician who is passionate about reshaping how we approach prevention, behavior change, and metabolic health. A Forbes 30 Under 30 honoree, she’s helped over 150,000 people improve their metabolic health using tools like continuous glucose monitors and behavior-focused nutrition strategies. Kara has been featured by Forbes, UC Berkeley, and HLTH, and has appeared on top podcasts like Mind Pump and The Genius Life.




